Mechanism of Radiation
What is radiation?
Radiation is high-speed particles and high-energy electromagnetic waves that are emitted when an atomic nucleus is split etc. It is invisible and intangible.
Types of radiation
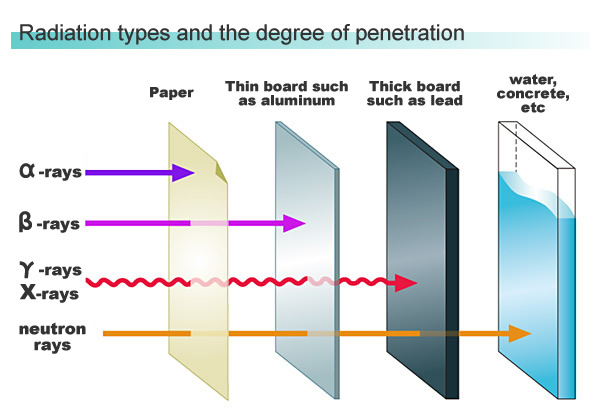
Types of radiation include alpha (α) rays, beta (β) rays, gamma (γ) rays, X rays, and neutron rays. A characteristic of radiation is that it can pass through objects, the degree of penetration varying according to the type of radiation and other conditions. This property is taken advantage of in the use of radiation for inspection and survey purposes. X rays, first observed by a scientist named Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895, are now familiar to us, since they are commonly used for physical examinations. However, if exposed to a massive dose of radiation, the human body is injured. In the case of atomic bombs, it is said that gamma rays and neutron rays caused the most serious injury to the victims’ bodies.
A-bomb radiation and its impact on humans
Many A-bomb victims were exposed not only to the initial radiation that was released instantly when the bomb exploded, but also to residual radiation. Residual radiation includes the radioactive particles that fall to earth following a nuclear explosion (so-called “radioactive fallout” or “ashes of death”) and the rain that contains such radioactive materials (so-called “black rain”).
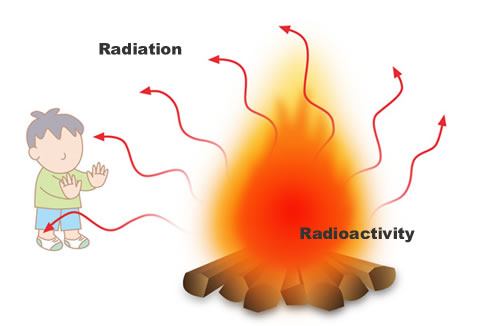
Difference between radiation and radioactivity
Radiation is emitted from radioactive materials. Radioactivity is the capacity of radioactive materials to emit radiation. Thinking like this will help you better understand: Radioactivity would correspond to the flames of a bonfire, whereas radiation is the heat emitted by the fire.